Research Summary
Lead researcher charged with the design of an SDN-ready city-scale 5G network for autonomous vehicles, which is critical for Innovate UK-funded projects. I designed a novel low-latency open-source road-side and on-board ITS-G5 DSRC (IEEE 802.11p/px) family of devices. These devices have being deployed across our campus.
I have a strong track record in Embedded Systems for 5G applications, Large-Scale Network Deployments for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles, Coding Theory and Mathematical Optimisation of heterogeneous networks - leading to 50 publications (19 journal, 29 conference papers and 2 book chapters). My contributions to the field of autonomous vehicles received the IEEE Best Paper Award at the SigTelCom 2017 and the IEEE Popularity Award at the IEEE VNC 2018. In addition, I have given several invited talks in national and international research centres, and I was an invited speaker at the prestigious 37th Wireless World Research Forum on the topic of next-generation networks for automotive applications.
Interests
- 5G Networks
- Self-driving Vehicles
- Energy efficient architectures
- Scalable real-time communications
- Resource allocation modeling
- Multi-tier system design
Talks
-
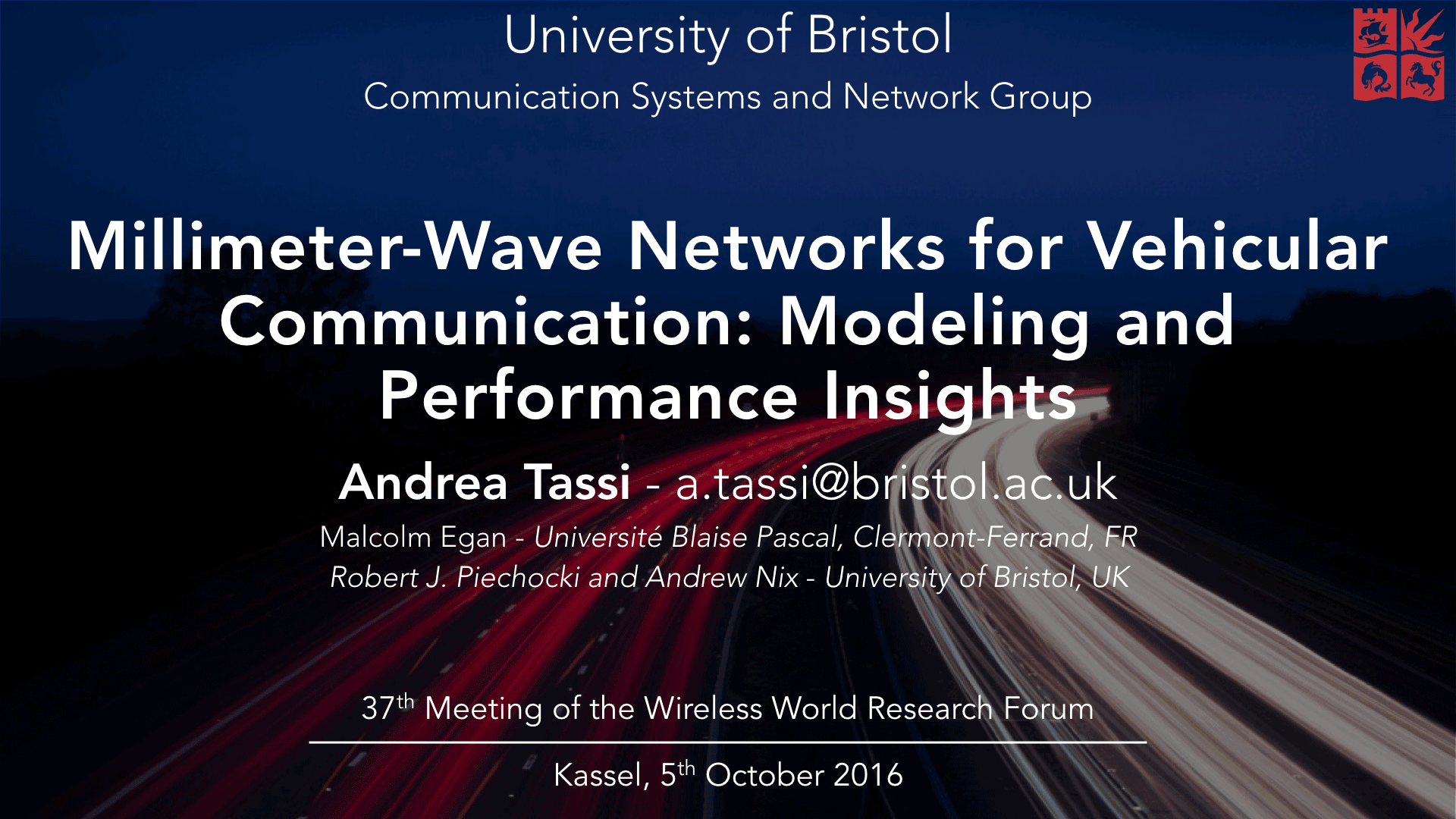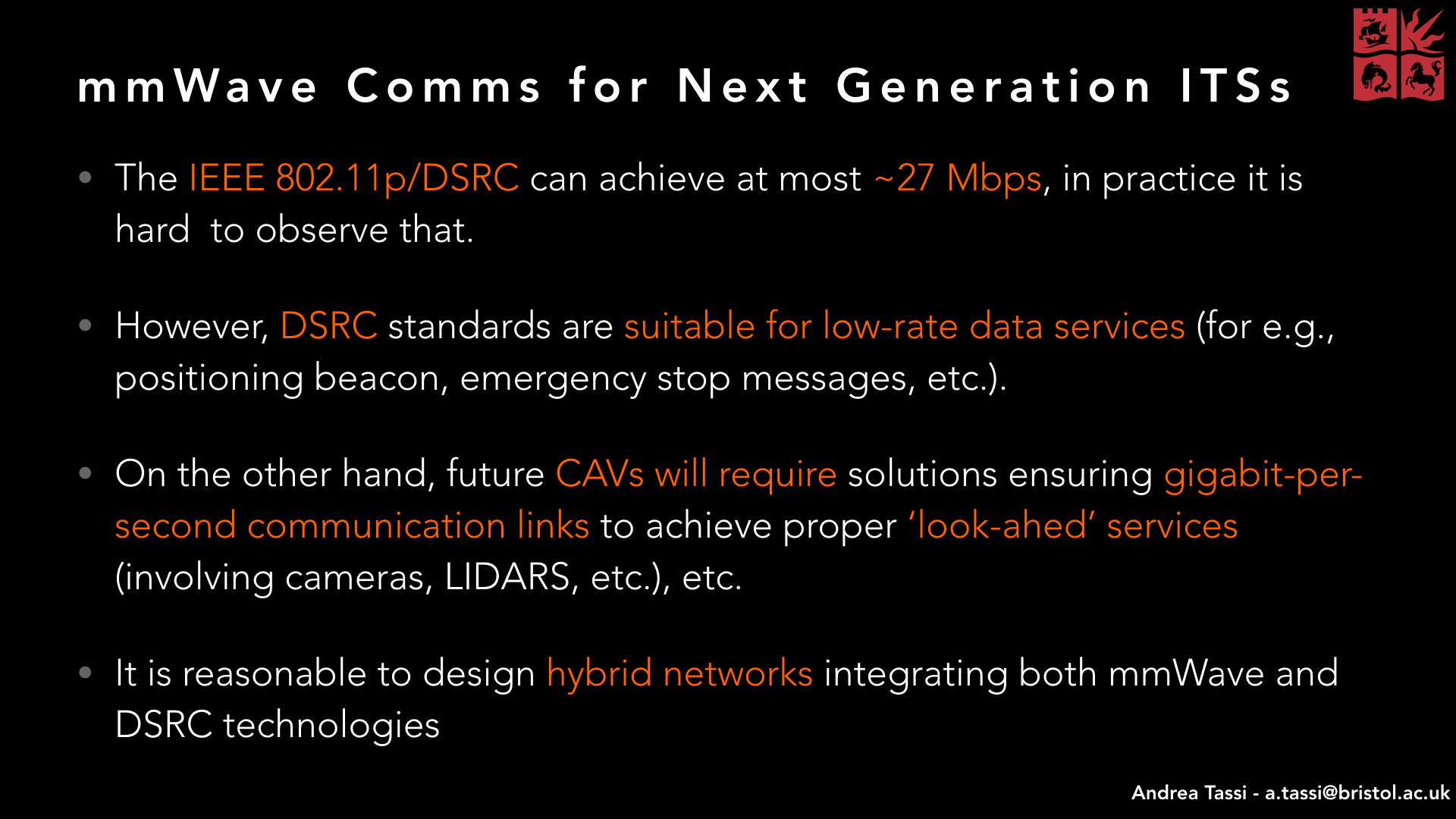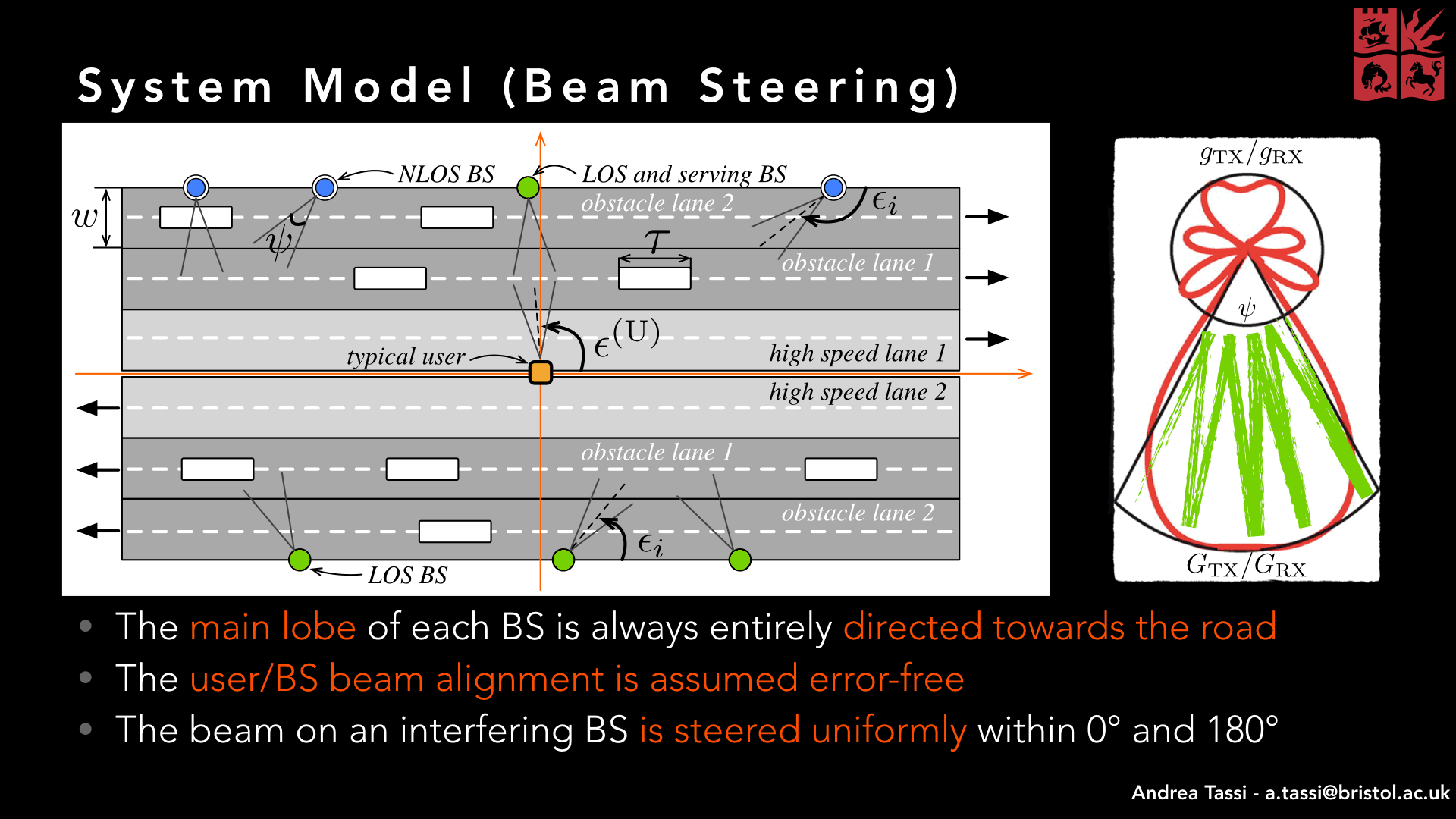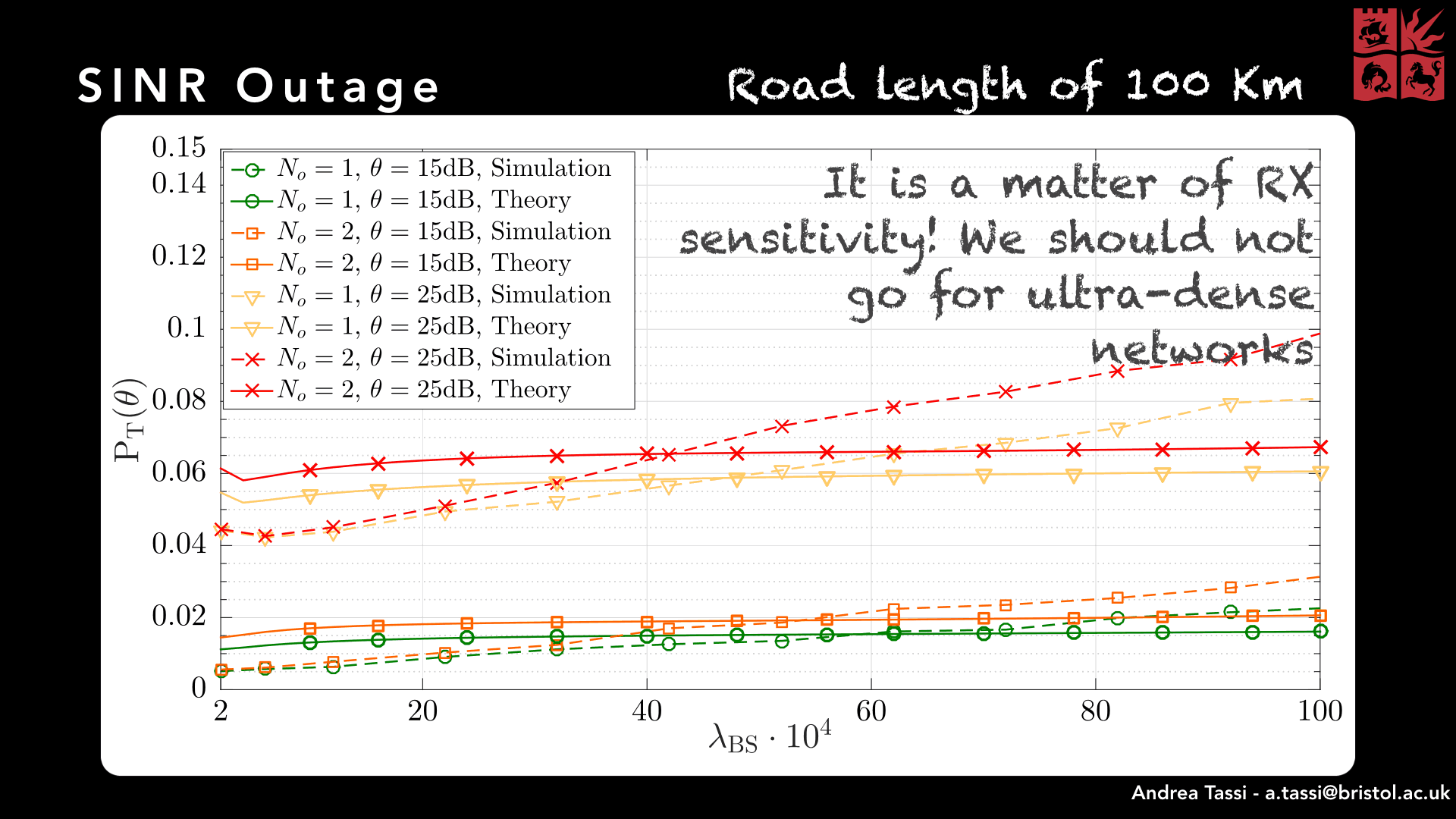
Abstract - Connected and autonomous vehicles will play a pivotal role in future Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSs) and smart cities, in general. High-speed and low-latency wireless communication links will allow municipalities to warn vehicles against safety hazards, as well as support cloud-driving solutions to drastically reduce traffic jams and air pollution. To achieve these goals, vehicles need to be equipped with a wide range of sensors generating and exchanging high rate row-data streams. Recently, millimeter wave (mmWave) techniques have been introduced as a means of fulfilling such high data rate requirements. In this tutorial, we will show how to model a highway communication network and characterize its fundamental link budget metrics. To evaluate our highway network, we will refer to a new theoretical model that accounts for a typical scenario where heavy vehicles (such as buses and lorries) in slow lanes obstruct Line-of-Sight (LOS) paths of vehicles in fast lanes and, hence, act as blockages. Our analysis will provide new design insights for mmWave highway communication networks. In particular, we will show that smaller antenna beamwidths and, unlike bi-dimensional mmWave cellular networks, smaller BS densities do not necessarily have a disruptive impact on improving the SINR outage probability, and consequently the rate coverage probability.
-

Abstract - OpenAirInterface (OAI) is a flexible open-source emulation platform and integrated tool to enable large-scale networking experimentation of 4G/5G systems. The SDR platform emulates a realistic system in a controlled and real-time environment, capable of interacting with external elements, such as commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) devices and testing equipments, and allowing validation and performance evaluation of novel approaches and technologies, including cloud RANs, application of SDN principles, massive MIMO and full-duplex communications. In this talk, we will cover the main aspects of OAI, and illustrate how to set up and operate a small-scale 3GPP LTE network consisting of emulated RAN and EPC entities providing connectivity to a COTS UE.
-

Abstract - Self-driving vehicles are expected to become a viable and effective solution for reducing the huge number of deaths caused by road accidents. That imposes vehicles to be equipped with a huge number of sensors, which are supposed to exchange high data rate row data streams. In our system model, that is made possible by millimeter-Wave (mmWave) communication links. By resorting to stochastic geometrical results, we propose a novel theoretical performance model for characterizing the Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (SINR) outage probability and the downlink communication rate coverage probability of users driving along a highway section. Being mmWave Base Stations (BSs) placed at the side of a multi-lane road section, users are likely to be surrounded by large-footprint vehicles, which behaves as blockages. The proposed model characterizes blockage positions as following multiple independent mono-dimensional Poisson point processes, which have a direct impact on the proposed line-of-sight/non-line-of-sight model. The numerical results show that the proposed theoretical model can efficiently describe the network performance, for different antenna patterns, array gains and road layouts. In addition, we will observe how the antenna beamwidth does not necessarily have a disruptive impact on the the SINR outage probability, and hence, on the rate coverage probability. Furthermore, we will also observe how the BSs density does not largely affect the network performance, as happens in bi-dimensional mmWave cellular networks.
-
Abstract - Self-driving vehicles are expected to become a viable and effective solution for reducing the huge number of deaths caused by road accidents. That imposes vehicles to be equipped with a huge number of sensors, which are supposed to exchange high data rate row data streams. In our system model, that is made possible by millimeter-Wave (mmWave) communication links. By resorting to stochastic geometrical results, we propose a novel theoretical performance model for characterizing the Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (SINR) outage probability and the downlink communication rate coverage probability of users driving along a highway section. Being mmWave Base Stations (BSs) placed at the side of a multi-lane road section, users are likely to be surrounded by large-footprint vehicles, which behaves as blockages. The proposed model characterizes blockage positions as following multiple independent mono-dimensional Poisson point processes, which have a direct impact on the proposed line-of-sight/non-line-of-sight model. The numerical results show that the proposed theoretical model can efficiently describe the network performance, for different antenna patterns, array gains and road layouts. In addition, we will observe how the antenna beamwidth does not necessarily have a disruptive impact on the the SINR outage probability, and hence, on the rate coverage probability. Furthermore, we will also observe how the BSs density does not largely affect the network performance, as happens in bi-dimensional mmWave cellular networks.
-

Abstract - Point-to-Multipoint communications are expected to play a pivotal role in next-generation networks. This talk refers to a cellular system transmitting layered multicast services to a Multicast Group (MG) of users. Reliability of communications is ensured via different Random Linear Network Coding (RLNC) techniques. We deal with a fundamental problem: the computational complexity of the RLNC decoder. The higher the number of decoding operations is, the more the user's computational overhead grows and, consequently, the faster the batteries of mobile devices drain. By referring to several sparse RLNC techniques, and without any assumption on the implementation of the RLNC decoder in use, we provide an efficient way to characterize the performance of users targeted by ultra-reliable layered multicast services. The proposed modeling allows to efficiently derive the average number of coded packet transmissions needed to recover one or more service layers. We design a convex resource allocation framework that allows to minimize the complexity of the RLNC decoder by jointly optimizing the transmission parameters and the sparsity of the code. The designed optimization framework also ensures service guarantees to predetermined fractions of users. Performance of the proposed optimization framework is then investigated in a LTE-A eMBMS network multicasting H.264/SVC video.
-
Abstract - In the near future, the delivery of multimedia multicast services over next-generation networks is likely to become one of the main pillars of future cellular networks. In this extended abstract, we address the issue of efficiently multicasting layered video services by defining a novel optimization paradigm that is based on an Unequal Error Protection implementation of Random Linear Network Coding, and aims to ensure target service coverages by using a limited amount of radio resources.
-

Abstract - The explosive growth of content-on-the-move, such as video streaming to mobile devices, has propelled research on multimedia broadcast and multicast schemes. Multi-rate transmission strategies have been proposed as a means of delivering layered services to users experiencing different downlink channel conditions. In this presentation, we consider multiple Unequal Error Protection implementations of the Network Coding strategy for their inherent reliability features. In addition, we formulate resource allocation frameworks which are capable of jointly optimizing both the NC scheme in use and the system transmission parameters. Our proposed frameworks are adapted to the LTE stack and the integrated eMBMS technology. Furthermore, we establish that the choice of the NC technique and the way we define a resource allocation model, play a critical role in the radio resource footprint associated with a multimedia service.
-

Abstract - The explosive growth of content-on-the-move, such as video streaming to mobile devices, has propelled research on multimedia broadcast and multicast schemes. Multi-rate transmission strategies have been proposed as a means of delivering layered services to users experiencing different downlink channel conditions. In this presentation, we consider random linear network coding for its inherent reliability features and study two encoding approaches, which are appropriate for layered services. We derive packet error probability expressions and use them as performance metrics in the formulation of resource allocation frameworks. The aim of these frameworks is both the optimization of the transmission scheme and the minimization of the number of broadcast packets on each downlink channel, while offering service guarantees to a predetermined fraction of users. Our proposed frameworks are adapted to the LTE stack and the integrated eMBMS technology. We focus on the delivery of a video service based on the H.264/SVC standard and demonstrate the advantages of layered network coding over multi-rate transmission. Furthermore, we establish that the choice of both the network coding technique and the resource allocation method play a critical role in the footprint of a service, as determined by the quality of each received video layer.
Research Projects
-

FLOURISH is a multi-sector collaboration, helping to advance the successful implementation of Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAVs) in the UK.
For more information http://www.flourishmobility.com/.
-

Leveraging state-of-the-art technologies, industry expertise and world-class academic research, the £5million VENTURER research and development project has over the last three years established the West of England as a centre of excellence for the safe user-led trialling of connected and autonomous vehicle (CAV) technology.
For more information https://www.venturer-cars.com/.
-

The R2D2 project aims at developing a mathematical framework to identify key relationships between various network parameters, contributing to the understanding of network dynamics and assisting in the system-level optimisation of network-coded architectures. In addition the project aims at leveraging the benefits of joint channel coding and network coding and propose novel transceiver designs for content delivery. Finally, it aims at delving into the emerging research field of network error correction and develop practical implementations of unified channel codes and network codes that can offer high reliability, low decoding complexity and increased security from malicious users.
For more information http://www.lancs.ac.uk/~chatzige/R2D2/.